基于php的助农生鲜销售系统的设计与实现
前言
在当前互联网时代,为了更好地促进农产品销售,帮助农民增收,基于 PHP 的助农生鲜销售系统应运而生。
该系统旨在搭建一座连接农民与消费者的桥梁,打破传统销售渠道的限制。从设计角度来看,系统注重用户体验和界面友好性。对于农民用户,提供了简单易懂的操作界面,方便他们上传生鲜产品信息,包括产品名称、产地、图片、价格、库存等详细内容,并能实时管理产品库存和销售订单。对于消费者而言,系统呈现出清晰的商品分类展示,如蔬菜、水果、肉类、蛋类等,方便快速查找所需生鲜。同时,配备了便捷的购物车功能和安全的支付系统,保障交易的顺利进行。
在实现方面,PHP 语言发挥了重要作用。它具有高效的开发效率和良好的数据库交互能力。系统利用 PHP 连接数据库,存储和管理大量的生鲜产品数据、用户信息以及交易记录等。通过 PHP 的逻辑处理能力,实现了订单处理、用户身份验证、优惠活动管理等关键功能。例如,在订单处理中,能够准确地记录订单状态、发货信息和物流跟踪。此外,系统还注重推广和营销功能的实现,通过社交媒体分享、会员制度等方式,提高助农生鲜销售系统的知名度和用户粘性,为农产品的销售开辟更广阔的市场,切实推动农业发展和农民增收致富,助力乡村振兴战略的实施。
详细视频演示
请联系我获取更详细的演示视频
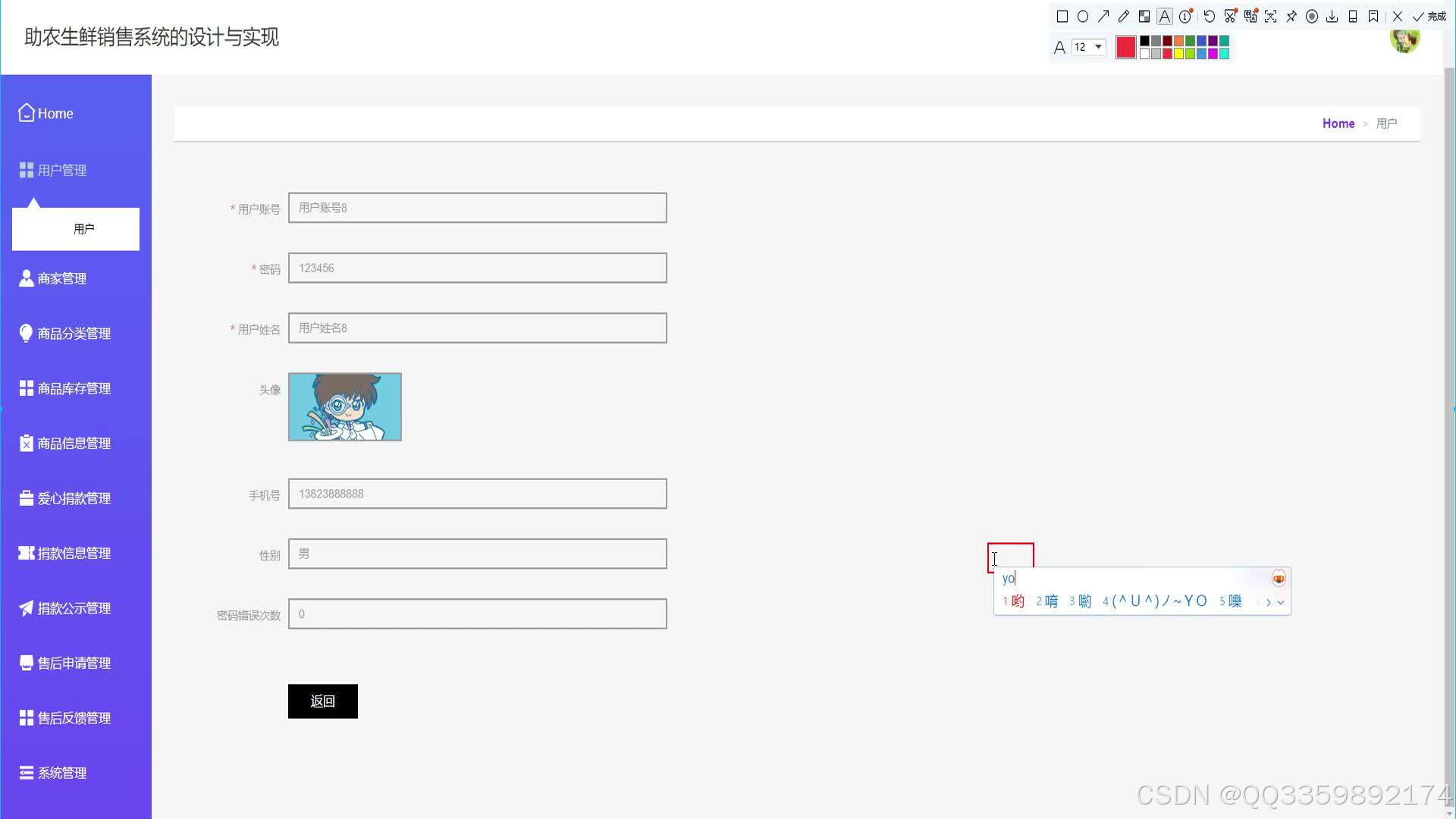
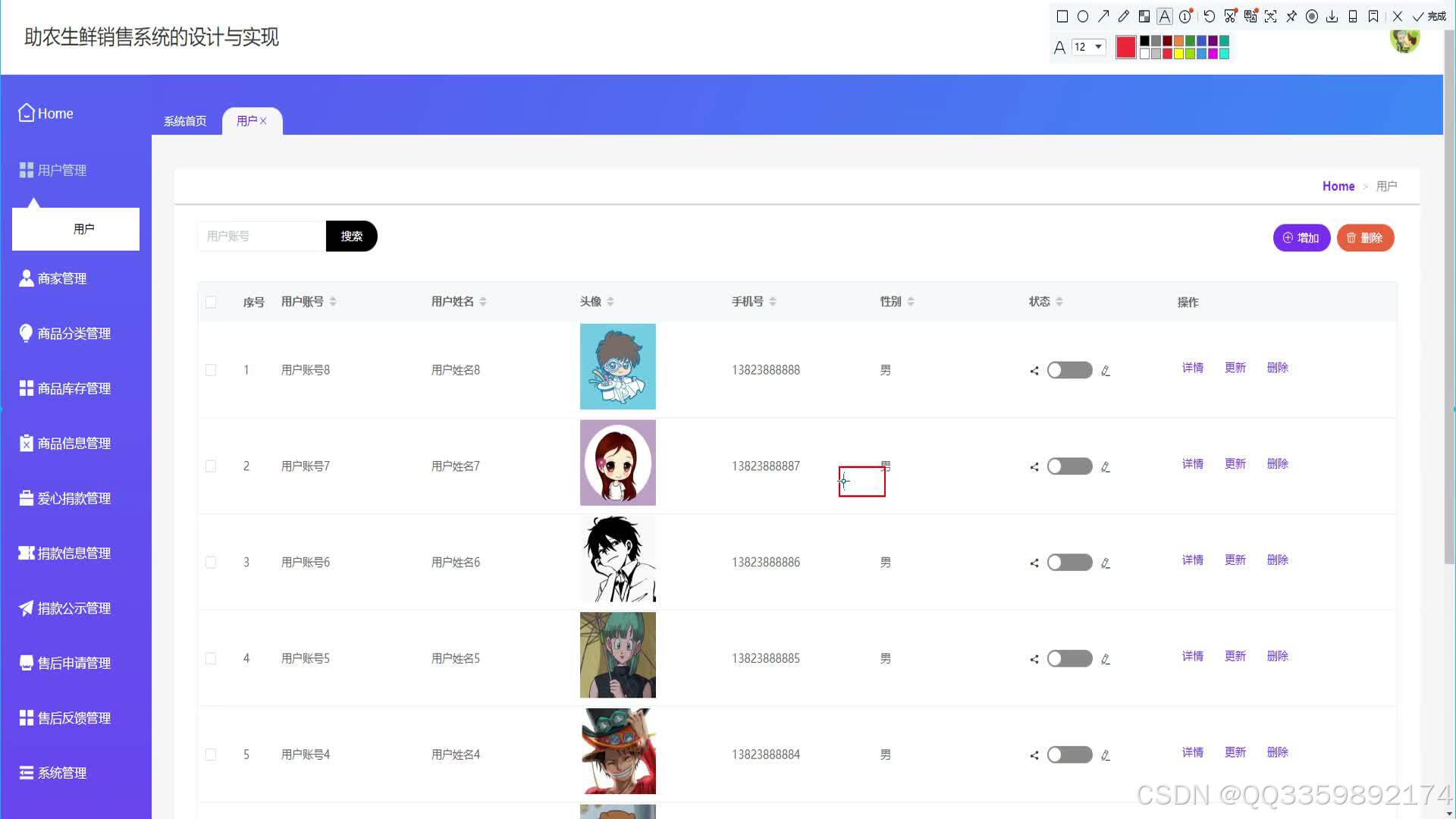
具体实现截图
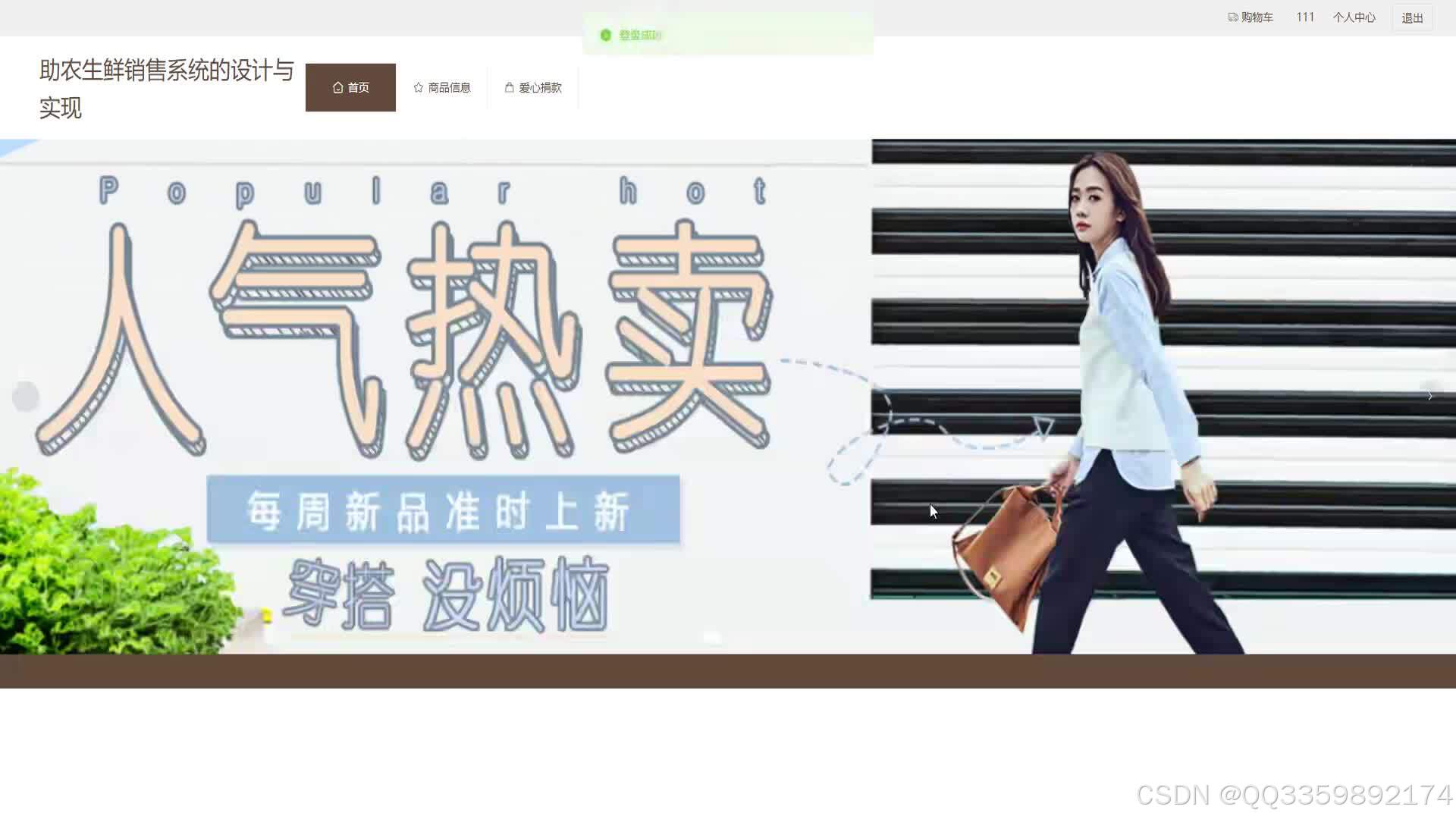
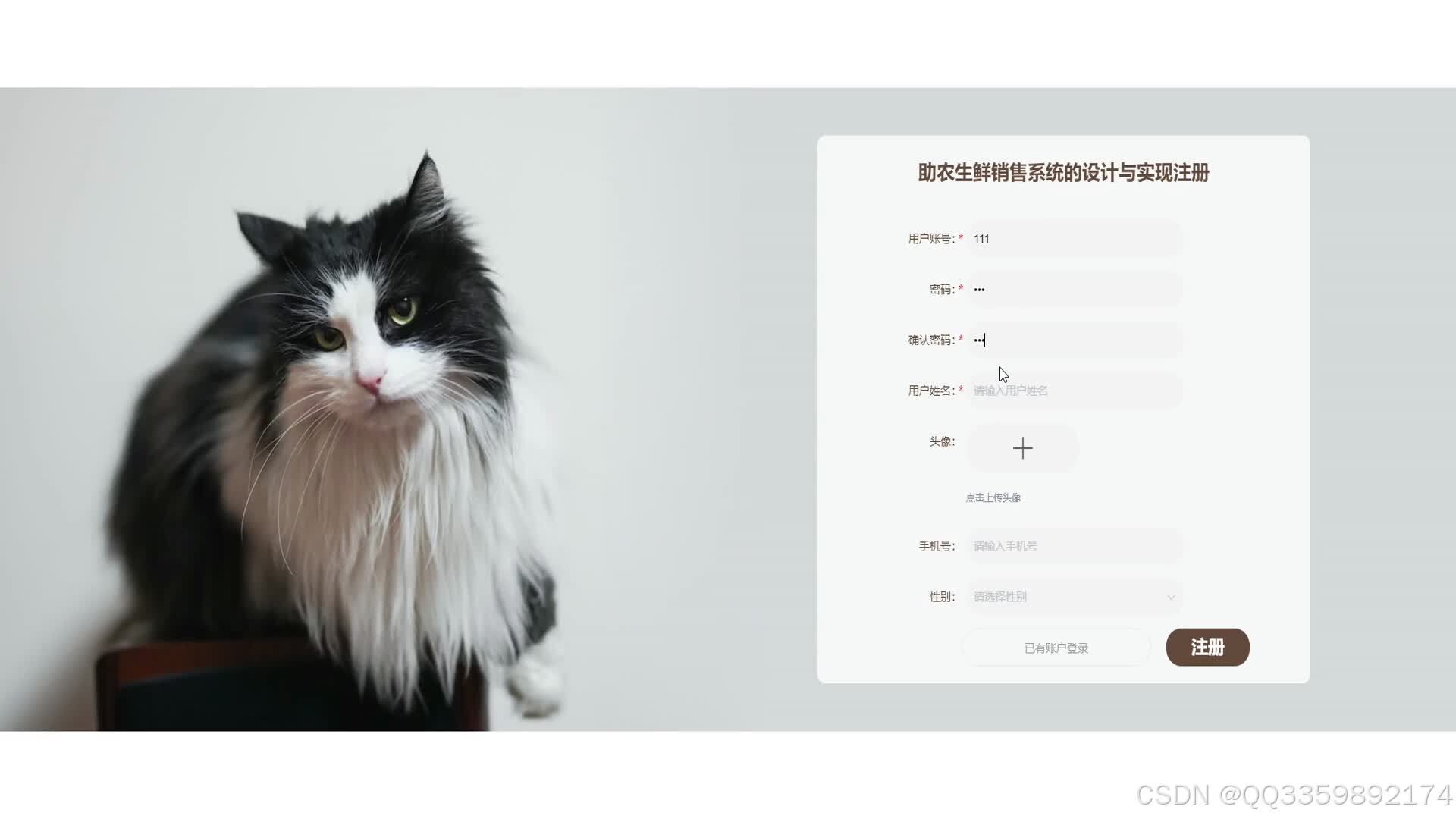
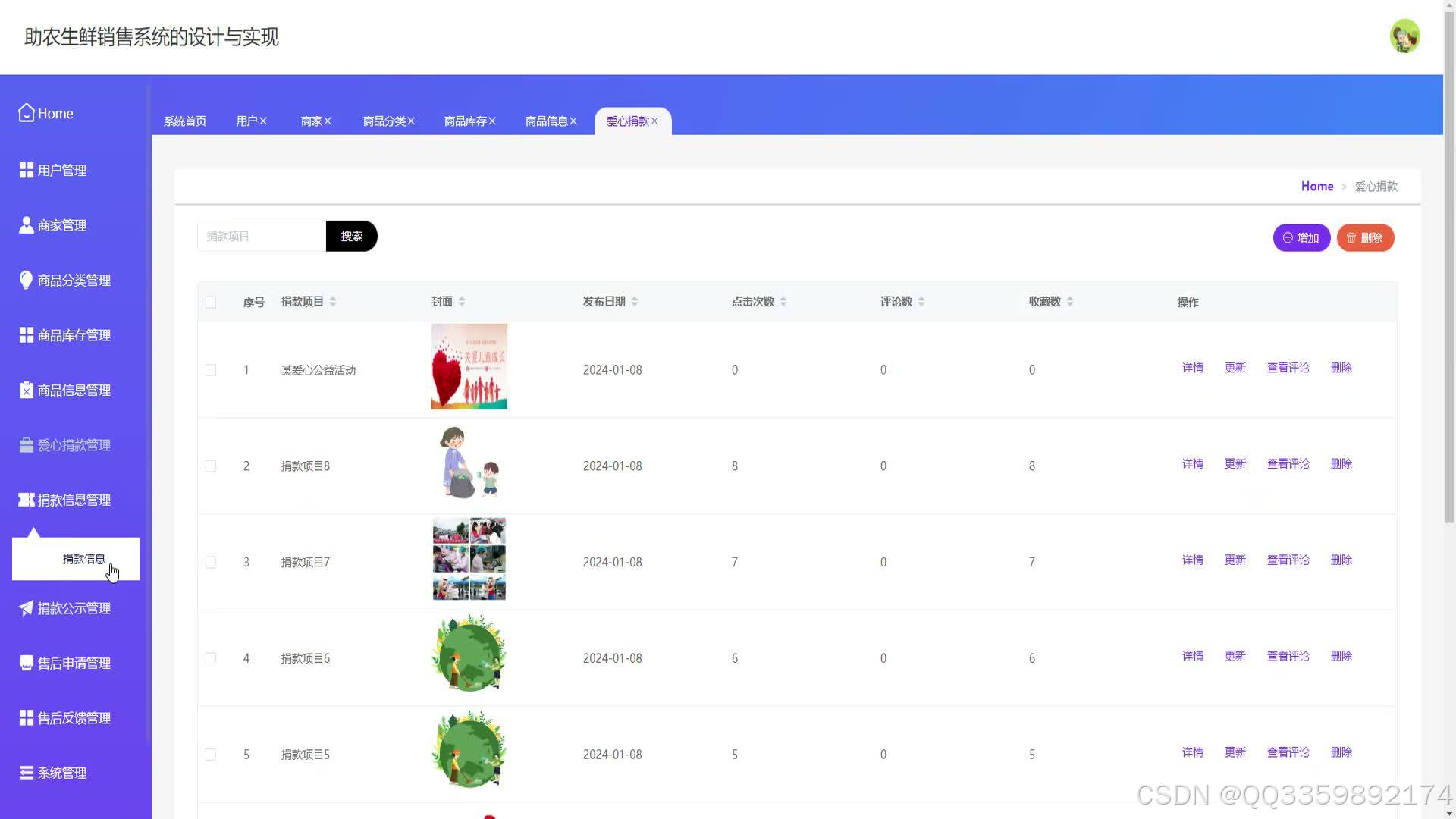
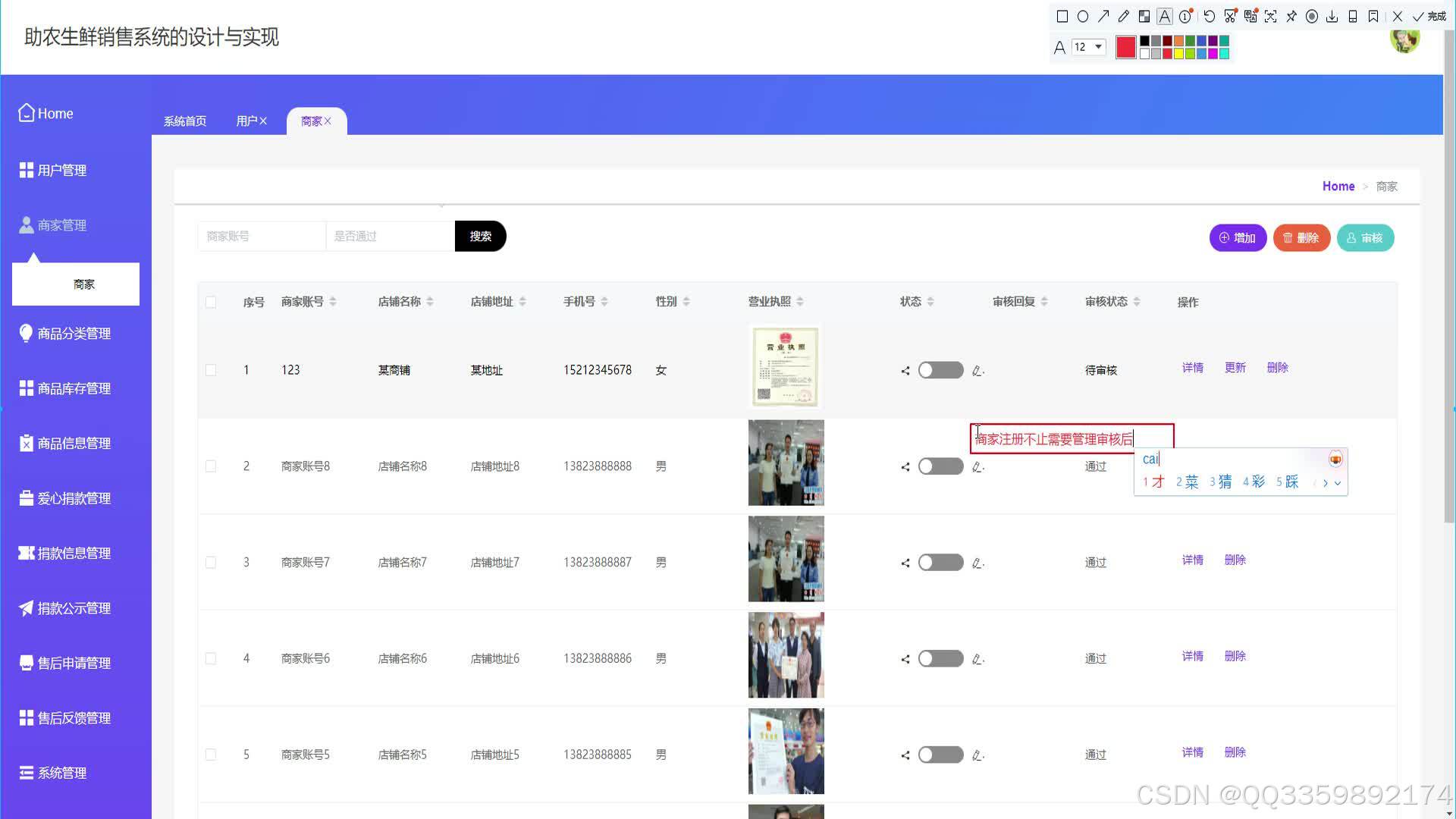
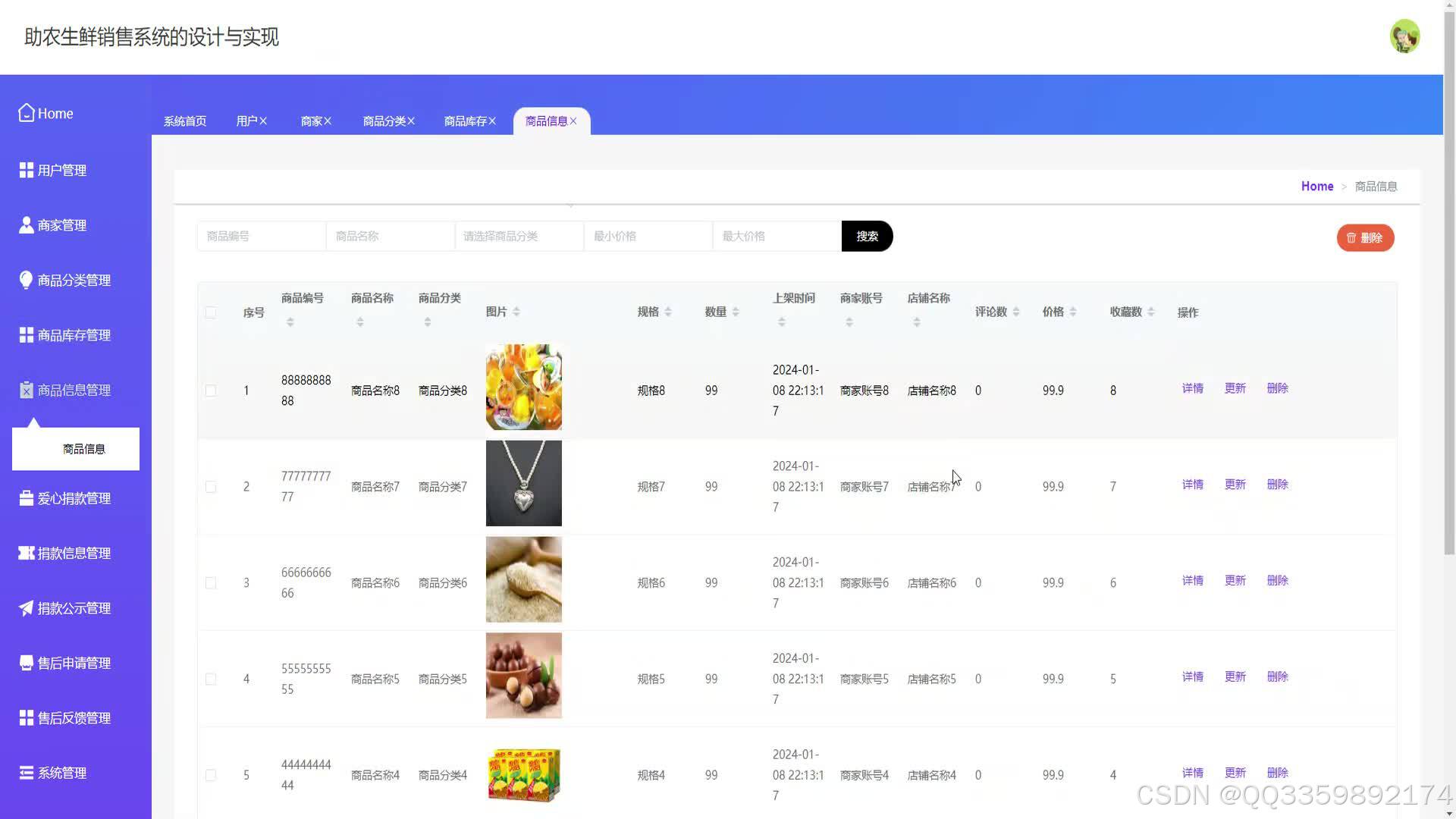
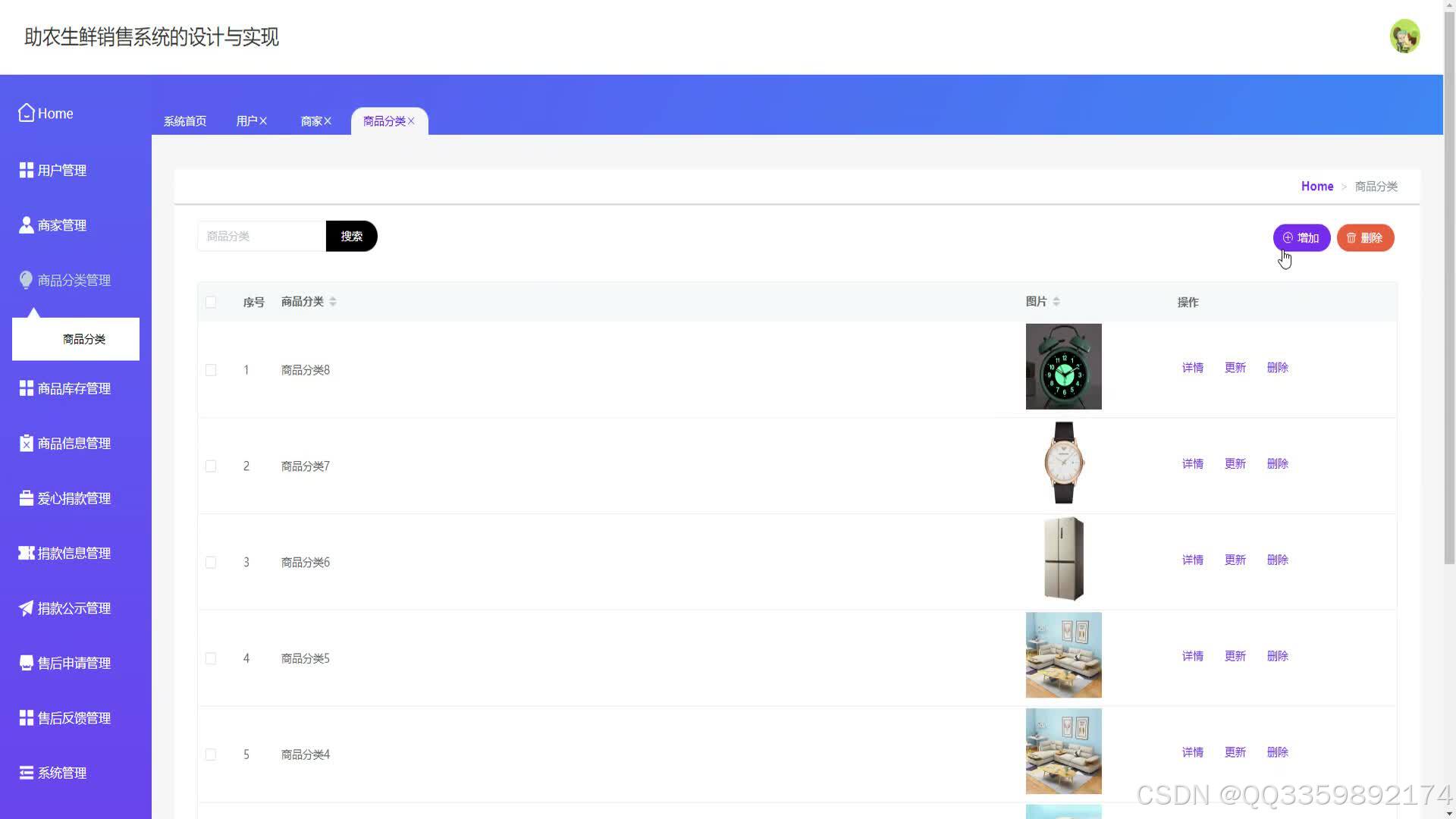
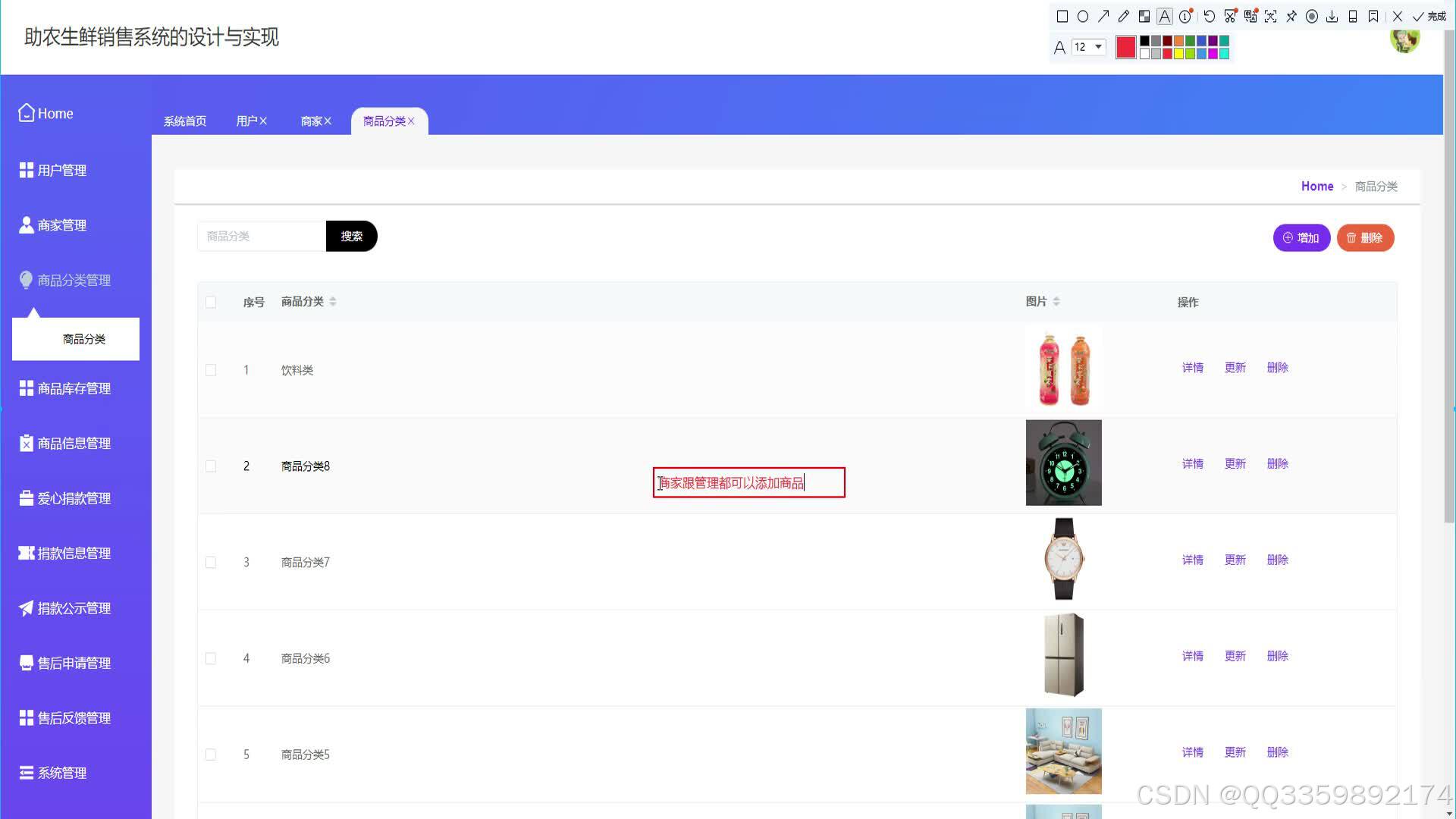

技术栈
后端框架SpringBoot
Spring Boot 是一种用于构建独立的、生产级的基于 Spring 框架的应用程序的框架。它的主要目标是简化 Spring 应用程序的开发过程,提供开箱即用的功能,同时保持核心的强大和灵活性。
Spring Boot 提供了一种快速开发应用程序的方式,通过自动配置和约定优于配置的原则,减少了开发人员编写样板代码的工作量。它的设计理念是“约定大于配置”,因此开发人员可以专注于业务逻辑的实现,而不是配置文件的编写。
Spring Boot 内置了嵌入式的 Web 服务器,如Tomcat、Undertow 或 Jetty,使得将应用程序打包成可执行的 JAR 文件成为可能。这样的设计使得应用程序的部署和运行变得非常简单,只需运行一个 java -jar 命令即可。同时,Spring Boot 也提供了丰富的 Actuator 支持,可以为应用程序提供运行时的监控和管理功能。
除此之外,Spring Boot 还提供了丰富的插件和扩展机制,可以轻松集成各种功能,如安全认证、数据访问、消息队列和缓存等。通过使用 Spring Boot Starter 起步依赖,开发人员可以轻松地添加需要的功能模块,并通过自动配置进行简单配置即可使用。
前端框架Vue
Vue.js是一款流行的JavaScript框架,用于构建用户界面(UI)和单页面应用程序(SPA)。它由尤雨溪于2014年创建,是一个轻量级、易于学习和灵活的框架。
Vue.js的核心优势在于其响应式数据绑定系统,使开发者能够轻松地管理视图和数据的变化。它还提供了一组简洁、直观的API,使开发过程更加高效和灵活。
Vue的组件化开发模式让开发者能够将应用拆分成小的、独立的组件,然后将这些组件组合成完整的应用程序。这种模式使得代码的重用性更高,维护和测试也更加容易。
另外,Vue.js还拥有一个非常活跃的社区,提供了许多好用的插件和工具,以及大量的文档和教程。这使得学习和使用Vue.js变得更加轻松和愉快。。
核心代码
package com;
import org.mybatis.spring.annotation.MapperScan;
import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication;
import org.springframework.boot.builder.SpringApplicationBuilder;
import org.springframework.boot.web.servlet.support.SpringBootServletInitializer;
@SpringBootApplication
@MapperScan(basePackages = {"com.dao"})
public class SpringbootSchemaApplication extends SpringBootServletInitializer{
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(SpringbootSchemaApplication.class, args);
}
@Override
protected SpringApplicationBuilder configure(SpringApplicationBuilder applicationBuilder) {
return applicationBuilder.sources(SpringbootSchemaApplication.class);
}
}
package com.controller;
import java.math.BigDecimal;
import java.text.SimpleDateFormat;
import java.text.ParseException;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Arrays;
import java.util.Calendar;
import java.util.Map;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Iterator;
import java.util.Date;
import java.util.List;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest;
import com.utils.ValidatorUtils;
import org.apache.commons.lang3.StringUtils;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.transaction.annotation.Transactional;
import org.springframework.format.annotation.DateTimeFormat;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.PathVariable;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestBody;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestParam;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
import com.baomidou.mybatisplus.mapper.EntityWrapper;
import com.baomidou.mybatisplus.mapper.Wrapper;
import com.annotation.IgnoreAuth;
import com.entity.YonghuEntity;
import com.entity.view.YonghuView;
import com.service.YonghuService;
import com.service.TokenService;
import com.utils.PageUtils;
import com.utils.R;
import com.utils.MPUtil;
import com.utils.MapUtils;
import com.utils.CommonUtil;
import java.io.IOException;
/**
* 用户
* 后端接口
* @author
* @email
* @date 2024-04-24 17:59:31
*/
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/yonghu")
public class YonghuController {
@Autowired
private YonghuService yonghuService;
@Autowired
private TokenService tokenService;
/**
* 登录
*/
@IgnoreAuth
@RequestMapping(value = "/login")
public R login(String username, String password, String captcha, HttpServletRequest request) {
YonghuEntity u = yonghuService.selectOne(new EntityWrapper<YonghuEntity>().eq("yonghuzhanghao", username));
if(u==null || !u.getMima().equals(password)) {
return R.error("账号或密码不正确");
}
String token = tokenService.generateToken(u.getId(), username,"yonghu", "用户" );
return R.ok().put("token", token);
}
/**
* 注册
*/
@IgnoreAuth
@RequestMapping("/register")
public R register(@RequestBody YonghuEntity yonghu){
//ValidatorUtils.validateEntity(yonghu);
YonghuEntity u = yonghuService.selectOne(new EntityWrapper<YonghuEntity>().eq("yonghuzhanghao", yonghu.getYonghuzhanghao()));
if(u!=null) {
return R.error("注册用户已存在");
}
Long uId = new Date().getTime();
yonghu.setId(uId);
yonghuService.insert(yonghu);
return R.ok();
}
/**
* 退出
*/
@RequestMapping("/logout")
public R logout(HttpServletRequest request) {
request.getSession().invalidate();
return R.ok("退出成功");
}
/**
* 获取用户的session用户信息
*/
@RequestMapping("/session")
public R getCurrUser(HttpServletRequest request){
Long id = (Long)request.getSession().getAttribute("userId");
YonghuEntity u = yonghuService.selectById(id);
return R.ok().put("data", u);
}
/**
* 密码重置
*/
@IgnoreAuth
@RequestMapping(value = "/resetPass")
public R resetPass(String username, HttpServletRequest request){
YonghuEntity u = yonghuService.selectOne(new EntityWrapper<YonghuEntity>().eq("yonghuzhanghao", username));
if(u==null) {
return R.error("账号不存在");
}
u.setMima("123456");
yonghuService.updateById(u);
return R.ok("密码已重置为:123456");
}
/**
* 后台列表
*/
@RequestMapping("/page")
public R page(@RequestParam Map<String, Object> params,YonghuEntity yonghu,
HttpServletRequest request){
EntityWrapper<YonghuEntity> ew = new EntityWrapper<YonghuEntity>();
PageUtils page = yonghuService.queryPage(params, MPUtil.sort(MPUtil.between(MPUtil.likeOrEq(ew, yonghu), params), params));
return R.ok().put("data", page);
}
/**
* 前台列表
*/
@IgnoreAuth
@RequestMapping("/list")
public R list(@RequestParam Map<String, Object> params,YonghuEntity yonghu,
HttpServletRequest request){
EntityWrapper<YonghuEntity> ew = new EntityWrapper<YonghuEntity>();
PageUtils page = yonghuService.queryPage(params, MPUtil.sort(MPUtil.between(MPUtil.likeOrEq(ew, yonghu), params), params));
return R.ok().put("data", page);
}
/**
* 列表
*/
@RequestMapping("/lists")
public R list( YonghuEntity yonghu){
EntityWrapper<YonghuEntity> ew = new EntityWrapper<YonghuEntity>();
ew.allEq(MPUtil.allEQMapPre( yonghu, "yonghu"));
return R.ok().put("data", yonghuService.selectListView(ew));
}
/**
* 查询
*/
@RequestMapping("/query")
public R query(YonghuEntity yonghu){
EntityWrapper< YonghuEntity> ew = new EntityWrapper< YonghuEntity>();
ew.allEq(MPUtil.allEQMapPre( yonghu, "yonghu"));
YonghuView yonghuView = yonghuService.selectView(ew);
return R.ok("查询用户成功").put("data", yonghuView);
}
/**
* 后台详情
*/
@RequestMapping("/info/{id}")
public R info(@PathVariable("id") Long id){
YonghuEntity yonghu = yonghuService.selectById(id);
return R.ok().put("data", yonghu);
}
/**
* 前台详情
*/
@IgnoreAuth
@RequestMapping("/detail/{id}")
public R detail(@PathVariable("id") Long id){
YonghuEntity yonghu = yonghuService.selectById(id);
return R.ok().put("data", yonghu);
}
/**
* 后台保存
*/
@RequestMapping("/save")
public R save(@RequestBody YonghuEntity yonghu, HttpServletRequest request){
if(yonghuService.selectCount(new EntityWrapper<YonghuEntity>().eq("yonghuzhanghao", yonghu.getYonghuzhanghao()))>0) {
return R.error("用户账号已存在");
}
yonghu.setId(new Date().getTime()+new Double(Math.floor(Math.random()*1000)).longValue());
//ValidatorUtils.validateEntity(yonghu);
YonghuEntity u = yonghuService.selectOne(new EntityWrapper<YonghuEntity>().eq("yonghuzhanghao", yonghu.getYonghuzhanghao()));
if(u!=null) {
return R.error("用户已存在");
}
yonghu.setId(new Date().getTime());
yonghuService.insert(yonghu);
return R.ok();
}
/**
* 前台保存
*/
@RequestMapping("/add")
public R add(@RequestBody YonghuEntity yonghu, HttpServletRequest request){
if(yonghuService.selectCount(new EntityWrapper<YonghuEntity>().eq("yonghuzhanghao", yonghu.getYonghuzhanghao()))>0) {
return R.error("用户账号已存在");
}
yonghu.setId(new Date().getTime()+new Double(Math.floor(Math.random()*1000)).longValue());
//ValidatorUtils.validateEntity(yonghu);
YonghuEntity u = yonghuService.selectOne(new EntityWrapper<YonghuEntity>().eq("yonghuzhanghao", yonghu.getYonghuzhanghao()));
if(u!=null) {
return R.error("用户已存在");
}
yonghu.setId(new Date().getTime());
yonghuService.insert(yonghu);
return R.ok();
}
/**
* 修改
*/
@RequestMapping("/update")
@Transactional
public R update(@RequestBody YonghuEntity yonghu, HttpServletRequest request){
//ValidatorUtils.validateEntity(yonghu);
if(yonghuService.selectCount(new EntityWrapper<YonghuEntity>().ne("id", yonghu.getId()).eq("yonghuzhanghao", yonghu.getYonghuzhanghao()))>0) {
return R.error("用户账号已存在");
}
yonghuService.updateById(yonghu);//全部更新
return R.ok();
}
/**
* 删除
*/
@RequestMapping("/delete")
public R delete(@RequestBody Long[] ids){
yonghuService.deleteBatchIds(Arrays.asList(ids));
return R.ok();
}
}
系统测试
从多个角度进行测试找到系统中存在的问题是本系统首要的测试目的,通过功能测试寻找出系统缺陷并改正,确保系统没有缺陷。在测试过程中证明系统满足客户需求,发现问题和不足及时改正。测试完成之后得出测试结论。
系统测试目的
在酒店管理系统的开发周期中,系统测试是必不可少且考验耐心的过程。其重要性在于,它是保证系统质量和牢靠性的最后一道关,也是整个系统开发过程的最后一次检查。
系统测试主要是为了避免用户在使用时发生问题,增强用户体验感,为了不影响用户的使用,我们需要从多角度、多思路去考虑系统可能遇到的问题,通过不同的模拟场景来发现缺陷并解决问题。在测试的过程中也可以了解到该系统的质量情况,系统功能是否健全,系统逻辑是否顺畅。一个合格的系统测试过程完成后将大大提升系统质量和使用感。测试的目标是验证系统是否符合需求规格说明书的定义,并找出与需求规格说明书不符合或与之冲突的内容。测试过程中一定站在用户的角度考虑问题,避免一些不切实际的场景,浪费测试时间,从而可能会引起问题导致预期结果与实际结果不符。
系统功能测试
对系统功能模块进行测试,通过点击、输入边界值和必填项非必填项的验证等方法进行一系列的黑盒测试。通过编写测试用例,根据测试用例中的内容进行测试,最后得出测试结论。
登录功能测试方案:当需要登入该系统时,通过账户密码等功能点进行验证,用户在输入时需要输入与数据库内存储的数据匹配的内容,当其中某项输入错误时系统将提示输入错误。此界面对角色权限也有相应的校验,当用户角色的帐号选择管理员角色登录时,也会报错。登录功能测试用例如下表所示。
系统测试结论
本系统主要使用黑盒测试,通过模拟用户使用系统实现各个功能编写测试用例,并进行测试。以确保系统流程的正确性。系统测试必不可少,可以使系统更加完善,该系统的可使用性也会更高。
测试该系统主要为了验证系统的功能模块是否满足我们最初的设计理念,验证各个功能模块逻辑是否正确,此系统不需要过于复杂的逻辑处理,以便于使用者操作。测试的最终目的也是围绕着用户使用展开。测试过程中所有场景都应符合用户需求,不可偏离需求目标,遇到问题时要站在用户的角度进行思考。经过一系列的测试过程后得到最终的测试结果,从测试结果可以看出,实现的系统在功能和性能方面满足设计要求。
源码获取
文章下方名片联系我即可~
✌💗大家点赞、收藏、关注、评论啦 、查看✌💗
👇🏻获取联系方式👇🏻
精彩专栏推荐订阅:在下方专栏👇🏻
- 本文标签: 其他
- 本文链接: http://www.7cjava.com/article/4814
- 版权声明: 本文由扬州梦语科技有限公司原创发布,转载请遵循《署名-非商业性使用-相同方式共享 4.0 国际 (CC BY-NC-SA 4.0)》许可协议授权










